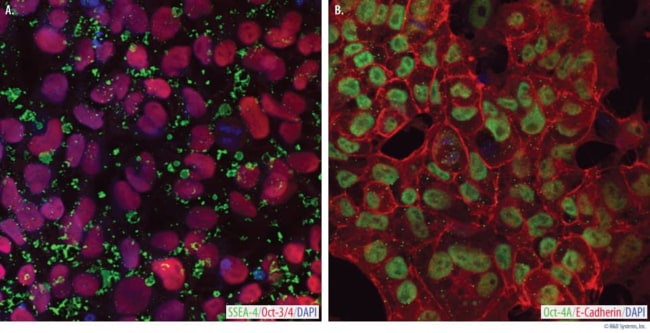
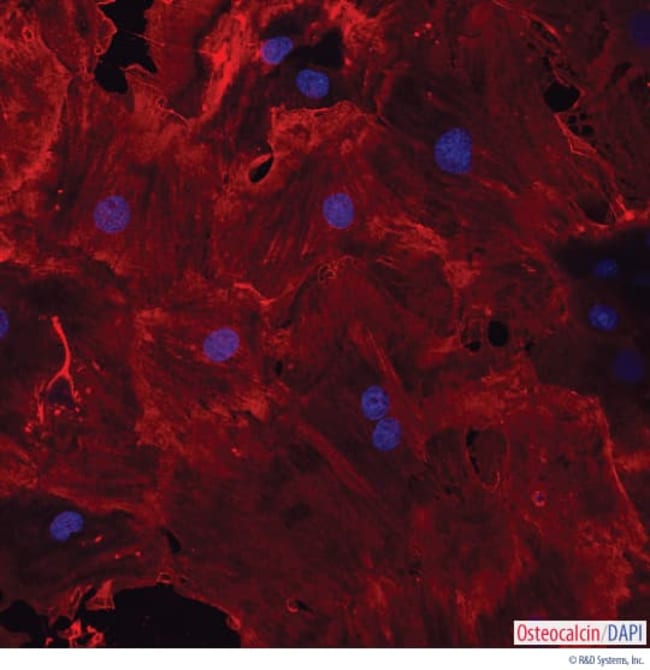
Stem Cell Culture Media
Explore our wide range of stem cell supplements and kits meticulously crafted to bolster growth, manipulation, and cryopreservation of diverse stem cell varieties. Our selection boasts an array of formulations and formats tailored to meet your specific needs. Whether you're working with embryonic, adult, or induced pluripotent stem cells, our collection caters to all.
Useful Links
Save Now - Exclusive Deals
Product Code 10315538
Product Code 15900263
Product Code 10601026
Product Code 7075762
Product Code 10438033
Product Code 17100636
Product Code 15400994
Product Code 11566351
Product Code 18411280
Product Code 18462050
Product Code 18431550
Product Code 11533590
Must Have
Product Code 15374799
Product Code 11580356
Product Code 15148645
Product Code 10212293
Product Code 9045085
Product Code 11586321
Product Code 16316592
Product Code 10115993
Complete Your Order - Great Deals
FAQ
The type of media used in stem cell culture depends on the specific type of stem cells being cultured. Here are some common media types:
Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs):
- mTeSR1 or mTeSR Plus: Defined, serum-free medium for human ESCs
- KnockOut™ DMEM/F-12: Often supplemented with KnockOut™ Serum Replacement, basic FGF (bFGF), and other additives
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs):
- Essential 8™ Medium: Chemically defined, xeno-free medium
- TeSR-E8: Another defined, xeno-free medium for human iPSCs
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs):
- DMEM (Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium): Often supplemented with 10-20% fetal bovine serum (FBS), L-glutamine, and antibiotics
- α-MEM (Alpha Minimum Essential Medium): Also supplemented similarly to DMEM
Neural Stem Cells (NSCs):
- Neurobasal™ Medium: Supplemented with B-27, N-2 supplements, EGF, and bFGF
- DMEM/F-12: Supplemented with N-2, B-27, and growth factors
Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs):
- StemSpan™ SFEM: Serum-free expansion medium, often supplemented with specific cytokines and growth factors
Cardiac Stem Cells:
- RPMI 1640: Often supplemented with B-27 and other specific factors
These media types are often supplemented with specific growth factors, cytokines, and other additives depending on the exact requirements of the stem cells being cultured.
Culturing stem cells involves several steps to ensure they grow and differentiate properly. A general guide:
- Ensure all equipment and workspaces are sterilized to prevent contamination
- Use specific culture media tailored to the type of stem cells being cultured (e.g., embryonic stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells, or adult stem cells)
- Coating with Matrix: Coat culture plates with an extracellular matrix protein (like Matrigel or laminin) to support cell attachment and growth
- Thawing: Quickly thaw frozen stem cell aliquots in a 37°C water bath
- Transfer the cells to a pre-coated culture dish with fresh culture medium
- Place the culture dishes in a humidified incubator set to 37°C with 5% CO2
- Change the culture medium every day or every other day to provide fresh nutrients and remove waste products
- Regularly inspect the cells under a microscope to check for confluency (usually 70-80% for passaging)
- Use enzymes like Trypsin-EDTA or non-enzymatic solutions to detach the cells from the culture dish
- Replate the cells at a lower density in fresh, pre-coated culture dishes with fresh medium
- For pluripotent stem cells: add specific growth factors or small molecules to the culture medium to maintain pluripotency (e.g., bFGF for embryonic stem cells)
- Differentiation (if needed): Change the culture conditions by adding specific factors to induce differentiation into desired cell types
- Quality Control: Regularly check for viability, contamination, and relevant markers
Specific protocols can vary depending on the type of stem cells and the experimental requirements. Always refer to detailed protocols and guidelines specific to your cell type and experimental setup.
Culturing stem cells can be challenging due to their specific requirements and sensitivity to environmental conditions. Here are some factors that contribute to the difficulty:
- Sterility: Maintaining a sterile environment is crucial to prevent contamination, which can be more challenging due to the frequent handling and medium changes required
- Nutrient Requirements: Stem cells often require specific nutrients, growth factors, and supplements tailored to their type (e.g., bFGF for pluripotent stem cells)
- Surface Coating: Proper adhesion and growth often necessitate coating culture surfaces with extracellular matrix proteins like Matrigel or laminin.
- Environmental Conditions: Maintaining precise temperature (37°C), CO2 levels (5%), and humidity is essential. Variations can negatively affect cell health and differentiation
- Passaging: Stem cells typically need to be passaged (sub-cultured) regularly to prevent over-confluency, which can lead to differentiation or cell death. This process requires careful handling to avoid damaging the cells
- Pluripotency Maintenance: For pluripotent stem cells (like ESCs and iPSCs), it's critical to maintain their undifferentiated state, which requires adding specific factors and regular monitoring
- Differentiation Control: If differentiation is the goal, precise control over the induction process and timing is necessary to achieve the desired cell types
Despite these challenges, with proper training, adherence to protocols, and attention to detail, stem cell culture can be successfully managed.